 What is Porter's 5 Forces Analysis?
What is Porter's 5 Forces Analysis?
Porter's 5 Forces model is a strategic analysis tool for analysing the competitive forces in an industry and determining the relative attractiveness of your position in it. It was developed by Michael E. Porter in 1979.
Why is Industry Analysis important?
Have you ever wondered why competitors in some industries always seem to struggle, while those in other industries seem to have a license to print money?
For example, airlines, railways and utilities always seem to struggle. Tech companies, on the other hand, often seem to have a license to print money.
Industry analysis, using Porter's 5 Forces, can help to understand which industries are most likely to be profitable, and how businesses can position themselves within those industries.
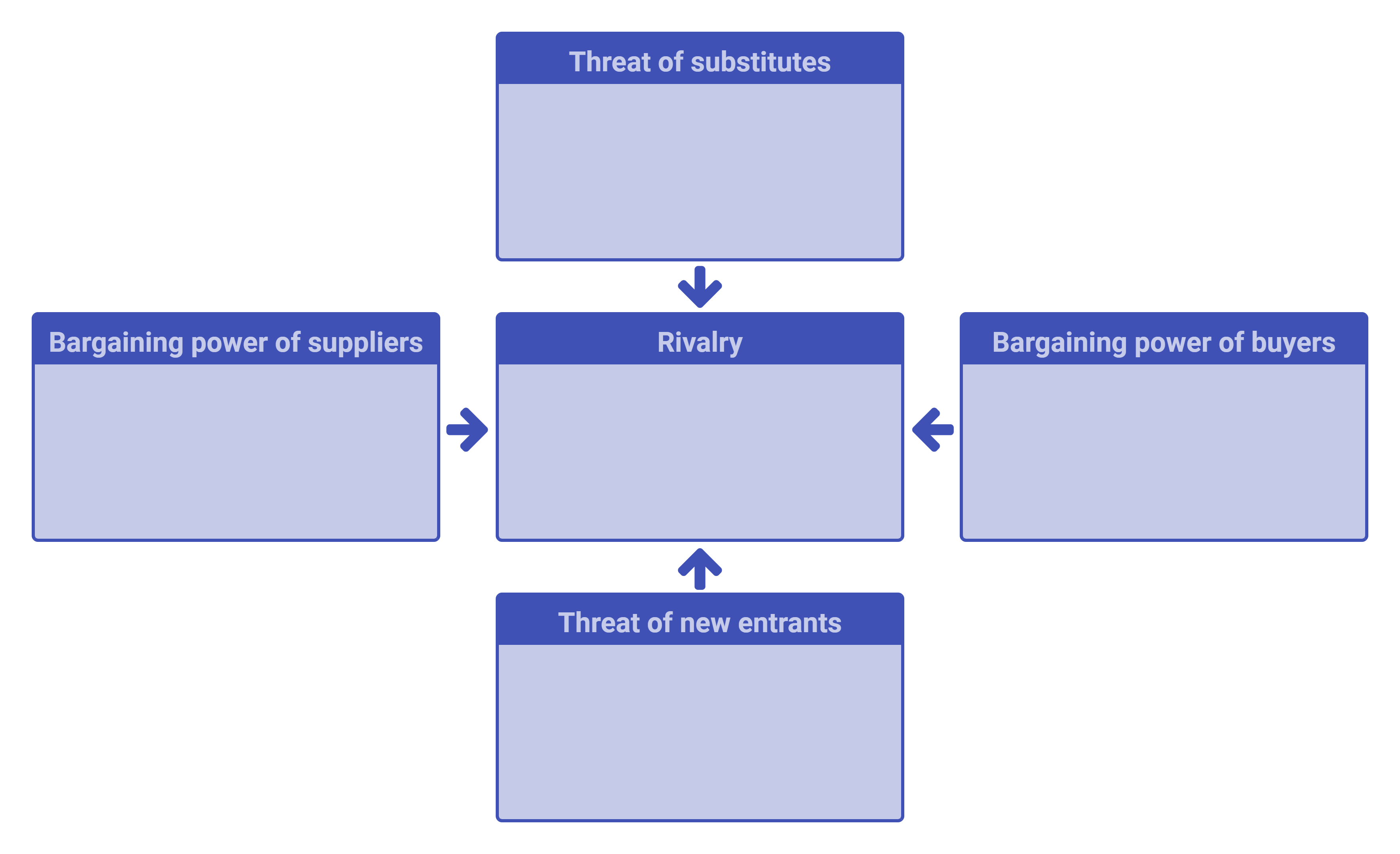
What are the 5 Forces of Industry Competitiveness?
Here is a breakdown of the five forces and how they impact industry competition.
Competitive Rivalry
Competitive rivalry assess intensity of competition among existing firms in an industry. A high level of rivalry can limit profitability as businesses may engage in price wars or increased marketing costs. It can also necessitate a need for ongoing, continuous - but expensive - innovation.
Industries with many competitors, low growth or low product differentiation often experience fierce rivalry. For example, the rivalry between Coca-Cola and Pepsi in the soft drink market illustrates how intense competition driver market and innovation.
Understanding this force helps in strategizing on differentiation or cost leadership to stand out in a crowded market.
Factors to consider:
- Concentration & stability
- Industry growth rates
- Scarcity of resources
- Differentiation versus commoditisation
You can also:
- map the factors of competition against your main competitors and competitor categories using a Blue Ocean Strategy Canvas
- use this to differentiate your business, reducing the competitive rivalry it faces.
Bargaining power of suppliers
Suppliers can exert significant influence on an industry, especially if they provide unique or highly essential inputs. When suppliers have few competitors, they can demand higher prices or more favourable terms, squeezing the profitability of businesses that rely on their goods or services. Industries dependent on specialised materials or services often face high supplier power, as seen in the tech sector where key components like semiconductors are controlled by a few companies
Businesses facing high bargaining power of suppliers might consider strategies like supplier partnerships, vertical integration, or diversification of supplier base to mitigate this risk.
Factors to consider:
- Extracting a higher margin
- Forward integrating: suppliers gaining control over and integrating with your competitors
- Firm:supplier concentration ratio
- Employee solidarity
Bargaining power of Buyers/distributors
The power of buyers refers to the ability of customers to influence pricing and terms. When buyers are few but purchase in large volumes, or when they can easily switch to competing products, they hold significant power. This force pushes businesses to lower prices or improve quality to maintain customer loyalty. Retail giants like Walmart often wield considerable buyer power, forcing suppliers to offer their best prices.
Businesses that face high bargaining power of buyers or distributors might consider strategies to build customer loyalty and lock them in through innovation.
Factors to consider:
- Price sensitivity
- Backward integration: customers gaining control over their supply.
- Switching costs
- Buyer:firm concentration ratio
Threat of new entrants
New entrants can disrupt market dynamics by introducing new capacity or innovation. The ease with which new players can enter a market depends on barriers like capital requirements, brand loyalty, and regulatory constraints. Industries with high entry barriers, such as pharmaceuticals, where extensive research and regulatory approval are required, typically experience lower threats from new entrants.
Factors to consider:
- Industry profitability
- Barriers to entry (scale-based, relationship-based or legal)
- See also: A Taxonomy of Moats
Threat of substitutes
Substitutes refer to products or services from outside the industry that can satisfy similar customer needs. The presence of viable substitutes limits an industry’s ability to raise prices and forces businesses to innovate to stay competitive. For instance, the growing popularity of health drinks poses a significant threat to traditional soft drink companies.
Factors to consider:
- Disruptive change
- Perceived level of differentiation
- Level of price/performance of substitute
- Ease of substitution (fungibility)
Some references add a 6th force, which may either be complementors, the government, regulators, disruptors or the public. In truth, you could extend the model to incorporate any significant stakeholder category.
When doing a Porter 5 Forces analysis, don't ignore that the various players may interact with each other. They could even collude. And they are likely to respond to strategic changes from the firm and from each other. The competitive forces in the 5 forces analysis may be constantly shifting. Game theory may help to uncover the likely patterns in such unstable competitive fields.
Example
This example 5 Forces analysis of the Airline industry helps to show why so many airlines struggle financially.
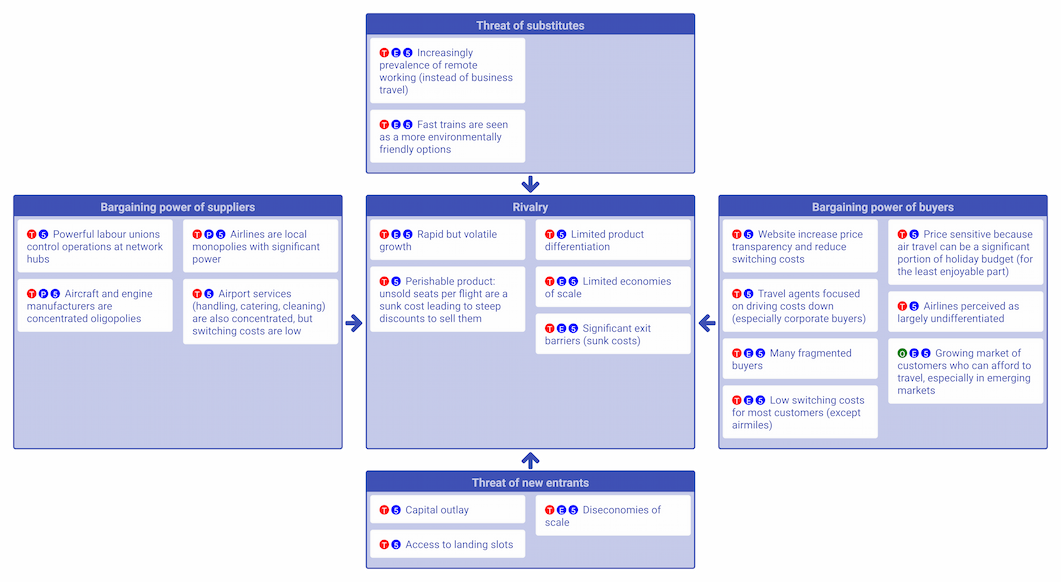
(Adapted from Michael Porter.)
Template
You could build your own 5 Forces analysis using StratNavApp.com. Gather and link your supporting evidence directly to your 5 Forces Analysis. Integrate your 5 Forces analysis into the rest of your strategic plan.
Where to find the 5 Forces Analysis in StratNavApp.com:
- Log In or Sign Up to StratNavApp.com
- Click "Analysis" on the Main Menu.
- Click "Insights" on the Drop Down Menu.
- Select "5 Forces" on the Selector at the top of the page that opens up.
StratNavApp.com's template is not a static, stand-alone template. The system will automatically integrate the insights from your Porter's 5 Forces analysis into the rest of your strategy. It will also help to ensure you review them all regularly so that your strategy remains responsive to changes in the industry in which you operate.
Once you've completed your Porter's 5 Forces Analysis you can also:
- Download it as an image to paste into another document, presentation or email by clicking the "download image" button
- see to the right and Downloading Images from StratNavApp.com
- Print it to paper or a PDF
- Include it in a strategy plan or report - see Generating Strategy Reports from StratNavApp.com
Getting the Balance Right
An advantage of frameworks like Porter's 5 Forces is that they may reveal biases in our thinking.
For example, if you have dozens of insights about the Bargaining Power of Customers, and few about the Bargaining Power of Suppliers, it may indicate a bias towards customers, and a blind spot regarding suppliers.
Our own research across hundreds of 5 Forces analyses shows that The Bargaining Power of Customers accounts for a full 50% of all 5 Forces insights. Does this indicate that organisations have become so customer-obsessed (a good thing in its own right) that they've stopped paying enough attention to the other 4 Forces (a potential blindspot)?
Of course, it may be that at this point in time and in your industry some forces really are more important than others, but it is at least worth considering whether you are suffering from a bias.
In Conclusion
Porter's Five Forces model is a powerful tool for understanding your industry's landscape. By analysing these forces, you can develop strategies that exploit opportunities and mitigate threats, ultimately leading to a more robust business strategy.
Interested in diving deeper into strategic business analysis? Sign Up or Log In to StratNavApp.com for tools and resources that can help you apply Porter's Five Forces to your business strategy.
See also:
- Working with Insights and Insight-based models
- Essential Strategic Analysis Tools
- A case study - Porter's 5 Forces: John Lewis defends it supplier rebate demand
- Porter's 1979 Harvard Business Review article on How Competitive Forces Shape Strategy.
- Navigating The Turbulence: Airlines, PESTLE, 5 Forces, And The Call For Paradigm Shift (Sixcess Consulting)
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are Porter's 5 Forces of Industry Competitiveness?
Porter's 5 Forces of industry competitiveness are (1) the Competitive Power of Buyers, (2) the Threat of Substitutes, (3) the Threat of New Entrants, (4) Competitive Rivalry and (5) the Bargaining Power of Suppliers. Together they can help you understand the attractiveness of an industry position, and how to position yourself in it. Learn more in this comprehensive article.
What is Porter's 5 Forces Analysis?
Porter's 5 Forces Analysis is a strategic tool used to identify and analyze the competitive forces that shape every industry, determining its profitability and market attractiveness.
What are the 5 forces in Porter's model?
The five forces in Porter's model include Competitive Rivalry, Threat of New Entrants, Bargaining Power of Suppliers, Bargaining Power of Customers, and Threat of Substitute Products or Services.
How do you perform a Porter's 5 Forces Analysis?
To perform a Porter's 5 Forces Analysis, assess each of the five forces in relation to your industry, determine the strength of each force, and identify how these forces affect your company's profitability and strategy.
Why is Porter's 5 Forces Analysis important?
Porter's 5 Forces Analysis is important because it helps businesses understand the factors influencing competition in their industry, allowing them to develop effective strategies for maintaining or increasing market share.
Can you use a template for Porter's 5 Forces Analysis?
Yes, you can use a template for Porter's 5 Forces Analysis. The article provides a free template that guides you through assessing each force and its impact on your business strategy.
